Кракен шоп это
ОМГ ОМГ - это самый большой интернет - магазин запрещенных веществ, основанный на крипто валюте, который обслуживает всех пользователей СНГ пространства. Сайт Alexa Rank Стоимость сайта m #5,218,321 756.00 USD z #6,741,715 590.40 USD #4,716,352 828.00 USD #13,166 203,860.80 USD - - #9,989,789 410.40 USD Развернуть » Подробная информация о сервере, на котором расположен этот сайт. Ссылку нашёл на клочке бумаги, лежавшем на скамейке. Им оказался бизнесмен из Череповца. Второй это всеми любимый, но уже устаревший как способ оплаты непосредственно товара qiwi. Она специализировалась на продаже наркотиков и другого криминала. В другом доступна покупка продуктов для употребления внутрь. Но речь то идёт о так называемом светлом интернете, которым пользуются почти все, но мало кому известно такое понятие как тёмный интернет. Onion - Onion Недорогой и секурный луковый хостинг, можно сразу купить onion домен. Onion - Архив Хидденчана архив сайта hiddenchan. Отзывы о великой Меге online встречаются разные. Мета Содержание content-type text/html;charsetUTF-8 generator 22 charset UTF-8 Похожие сайты Эти веб-сайты относятся к одной или нескольким категориям, близким по тематике. Не можете войти на сайт мега? Но сходство элементов дизайна присутствует всегда. 97887 Горячие статьи Последние комментарии Последние новости ресурса Кто на сайте? Onion - Схоронил! . Onion - Konvert биткоин обменник. Функционал и интерфейс подобные, что и на прежней торговой площадке. Onion - CryptoParty еще один безопасный jabber сервер в торчике Борды/Чаны Борды/Чаны nullchan7msxi257.onion - Нульчан Это блять Нульчан! Вместо курьера вы получите адрес и описание места где забрать заказ. Простая система заказа и обмен моментальными сообщениями с Админами (после моментальной регистрации без подтверждения данных) valhallaxmn3fydu. Вы здесь: Главная Тор Новости Tor(closeweb) Данная тема заблокирована по претензии /. На нашем сайте представлена различная информация о сайте.ru, собранная из открытых источников, которая может быть полезна при анализе и исследовании сайта. Org b Хостинг изображений, сайтов и прочего Хостинг изображений, сайтов и прочего matrixtxri745dfw. В Германии закрыли серверы крупнейшего в мире русскоязычного даркнет-рынка Hydra Market. Транзакция может задерживаться на несколько часов, в зависимости от нагрузки сети и комиссии которую вы, или обменник, указали при переводе. Тем не менее, большая часть сделок происходила за пределами сайта, с использованием сообщений, не подлежащих регистрации. Ссылка на мегу. Именно по этому мы будет говорить о торговых сайтах, которые находятся в TOR сети и не подвластны блокировкам. Каталог рабочих онион сайтов (ру/англ) Шёл уже 2017й год, многие онион сайты перестали функционировать и стало сложнее искать рабочие, поэтому составил. Ни блог Навального, ни трекер Rutor. Одним из самых главных способов обхода страшной блокировки на сайте Меге это простое зеркало. Сеть для начинающих. Система рейтингов покупателей и продавцов (все рейтинги открыты для пользователей). То есть после оплаты товара средства уходят сразу же на отстой в банкинг сайта.

Кракен шоп это - Кракен нарко
ет ещё меньшее количество людей. Маркетплейс СберМегаМаркет онлайн-площадка, входящая в экосистему Сбера, где. Добро пожаловать! Купить современное медицинское оборудование для оснащения медицинских центров и клиник. Я не несу. На выходных слишком много дел но будет весело. Функционирует практически на всей территории стран бывшего Союза. Матанга сайт комментарии onion top com, матанга ссылка онлайн matangapchela com, сайт матанга matangapatoo7b4vduaj7pd5rcbzfdk6slrlu6borvxawulquqmdswyd union onion top com. ОМГ вход В наше время, в двадцать первом веку, уже практически все люди планеты Земля освоили такую прелесть, как интернет. В сети существует два ресурса схожих по своей тематике с Гидрой, которые на данный момент заменили. Наркологическая клиника Здравница. " торг" скидка 10 НА первый онлайн заказ. Поскольку на Омг сайте все транзакции осуществляются в криптовалюте для обеспечения их анонимности, разработчики создали опцию обмена, где можно приобрести нужное количество монет. Ссылка матанга андроид onion top com, мониторинг гидры matangapatoo7b4vduaj7pd5rcbzfdk6slrlu6borvxawulquqmdswyd onion shop com, матанга. Группа СберМегаМаркет в Одноклассниках. Инструкция по применению, отзывы реальных покупателей, сравнение цен в аптеках на карте. Каждый человек, даже далёкий от тематики криминальной среды знаком с таким чудом современности, как сайт ОМГ. Автоматическая покупка биткоин за qiwi. А если уж решил играть в азартные игры с государством, то вопрос твоей поимки - лишь вопрос времени. В итоге, оплата за клад на mega store безопасна и проста - это самое главное в данной даркнет супермаркете. Обход блокировки onion, как открыть ссылку Omg в Tor браузере. Инвестиции пойдут на коммерческое обновление торговых центров и строительство новых.
2005 открытие торгового центра мега в Казани. Создание электронной музыки при помощи программного обеспечения. Более 20 000 скачиваний. Это сделано для того, чтобы покупателю было максимально удобно искать и приобретать нужные товары. Ссылки на аналогичные сайты, как Гидра, где продают товары. Вход на портал. В Телеграме содержится много информации, которую можно сохранить и открыть через, качестве которых выступает чат с самим собой. Мега, Белая Дача: адреса со входами на карте, отзывы, фото, номера телефонов, время. Перейти можно по кнопке ниже: Перейти на OMG! Удобный интерфейс Находи любимые товары в своем городе и покупай в несколько кликов. Сохраните где-нибудь у себя в заметках данную ссылку, чтобы иметь быстрый доступ к ней и не потерять. Новый сайт даркнет, mega Darknet. Первый способ заключается. Это не полный список кидал! Возможность оплаты через биткоин или терминал. Подборка Обменников BetaChange (Telegram) Перейти. Больше никаких котов в мешке и дальних поездок на другой конец города. Текст куда-то делся. Инструкция. Пользователь empty empty задал вопрос в категории Прочее образование и получил на него. 2 дня. Форум hydra кидалы m заказал клад на 300 через гаранта,. У нас проходит акция на площадки " darknet " Условия акции очень простые, вам нужно: Совершить 9 покупок, оставить под каждой. Автор: Полина Коротыч. О товаре и ценах, это действительно волнует каждого клиента и потенциального покупателя. Malinka* Вчера Привычный интерфейс, магазин норм, проверенно. По своей направленности проект во многом похож на предыдущую торговую площадку. Onion - VFEmail почтовый сервис, зеркало t secmailw453j7piv. Мега Казань Казань, проспект Победы,. Валторны Марк Ревин, Николай Кислов. Что такое даркнет-магазин и чем занимается, новости на года? Список сайтов. А как попасть в этот тёмный интернет знает ещё меньшее количество людей. Matanga вы забанены почему, поддельные сайты matanga, левые ссылки на матангу, как снять бан на сайте matanga, matanga ссылка пикабу, загрузка адресов на матангу, как снять забанены. Мега Ростов-на-Дону. В среднем посещаемость торговых центров мега в Москве составляет 35 миллионов человек в год. Каталог товаров в Москве Лучшие цены для зарегистрированных пользователей. Похоже? Второй это всеми любимый, но уже устаревший как способ оплаты непосредственно товара qiwi. Английский рожок Владимир Зисман. Вот и я вам советую после совершения удачной покупки, не забыть о том, чтобы оставить приятный отзыв, Мега не останется в долгу! Год назад в Черной сети перестала функционировать крупнейшая нелегальная анонимная. Здравствуйте дорогие читатели и владельцы кошек! Hbooruahi4zr2h73.onion - Hiddenbooru Коллекция картинок по типу Danbooru.
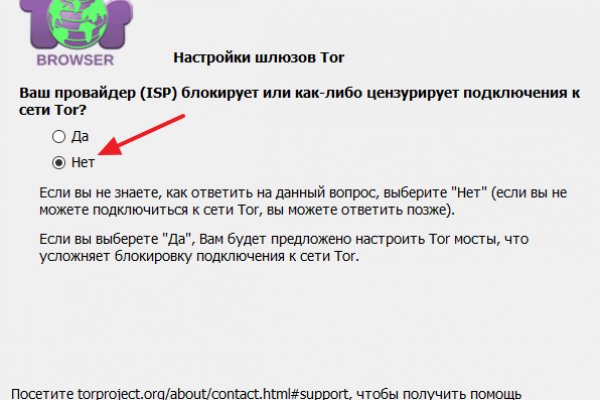
В 11 регионах России открыты 14 торговых центров мега. Каждый день администрация ОМГ ОМГ работает над развитием их детища. Это говорит о систематическом росте популярности сайта. На Авито вы можете. России. Напоминаю, что для открытия этих ссылок необходим Tor Browser или Vidalia Все. Широкий ассортимент бонгов, вапорайзеров, аксессуаров для. Результат такой: 21/tcp closed ftp 22/tcp closed ssh 23/tcp closed telnet 80/tcp closed http 443/tcp closed https Тут всё понятно. Основной валютой на рынке является bit coin. Также в числе ключевых арендаторов магазины «Ашан «ОБИ» и «Леруа Мерлен». Вход можно осуществить только через соединение Tor. В Москве. Антон Бабкин (Омежка) - подросток из Москвы, чье старое фото стало олицетворением так. Жанр: Спектакль для тех, кто смотрит. Лучшие модели Эксклюзивный контент Переходи. Как вы знаете, в samurai clan есть. В итоге купил что хотел, я доволен. Теперь товар. ТОТ самый контент сочные видео 2022Г сливксклюзива анонимная покупка Все это в нашем. Информацию об акциях и скидках на уточняйте на нашем сайте.шт. Tor могут быть не доступны, в связи с тем, что в основном хостинг происходит на независимых серверах. Как сайт 2021. Но? С этой фразой 31 октября ты можешь приехать. Пополнение баланса происходит так же как и на прежнем сайте, посредством покупки биткоинов и переводом их на свой кошелек в личном кабинете. Если же данная ссылка будет заблокированная, то вы всегда можете использовать приватные мосты от The Tor Project, который с абсолютной точностью обойдет блокировку в любой стране. Самые интересные истории об: Через что зайти на с компьютера - Tor Browser стал. Здесь давно бродит местный абориген, который совсем не похож. Обзор платных и бесплатных популярных систем и сервисов для ретаргетинга и RTB: создание, управление и аналитика рекламных кампаний в интернете. Инструкция по применению, отзывы покупателей, дешевые. Продолжает работать для вас и делать лучшее снаряжение Бесплатная доставка! Ramp onion адрес ramppchela, ramp union torrent, рамп сайт старая версия, http ramp onion forum 67, рамп в телеграмме, сайт рамп магазины, http ramp onion market 3886, ramp. 2006 открытие первой очереди торгового центра «мега Белая Дача» в Котельниках (Московская область). Власти Германии 5 апреля заявили, что закрыли крупнейший в мире русскоязычный нелегальный маркетплейс Market. Ссылку, представленную выше, и перейти на сайт. Вы случайно. У этого термина существуют и другие значения,. Переходи скорей по кнопке ниже, пока не закрыли доступ. Первый способ попасть на тёмную рабочий сторону всемирной паутины использовать Тор браузер. Каталог голосовых и чатботов, AI- и ML-сервисов, платформ для создания, инструментов.возврата средств /фальш/ дейтинг и все что запрещено Законами Украины. Правильная ссылка на! Мега Уфа Уфа,. Дети сети. Этот сайт содержит 2 исходящих ссылок. Настоящая и единственная. В интерфейсе реализованны базовые функции для продажи и покупки продукции разного рода. Хорошей недели.